🎶 Handpan Anatomy: Understanding the Structure and Sound

There is a diagram at the bottom of the article.
A First Look: The Flying Saucer Design
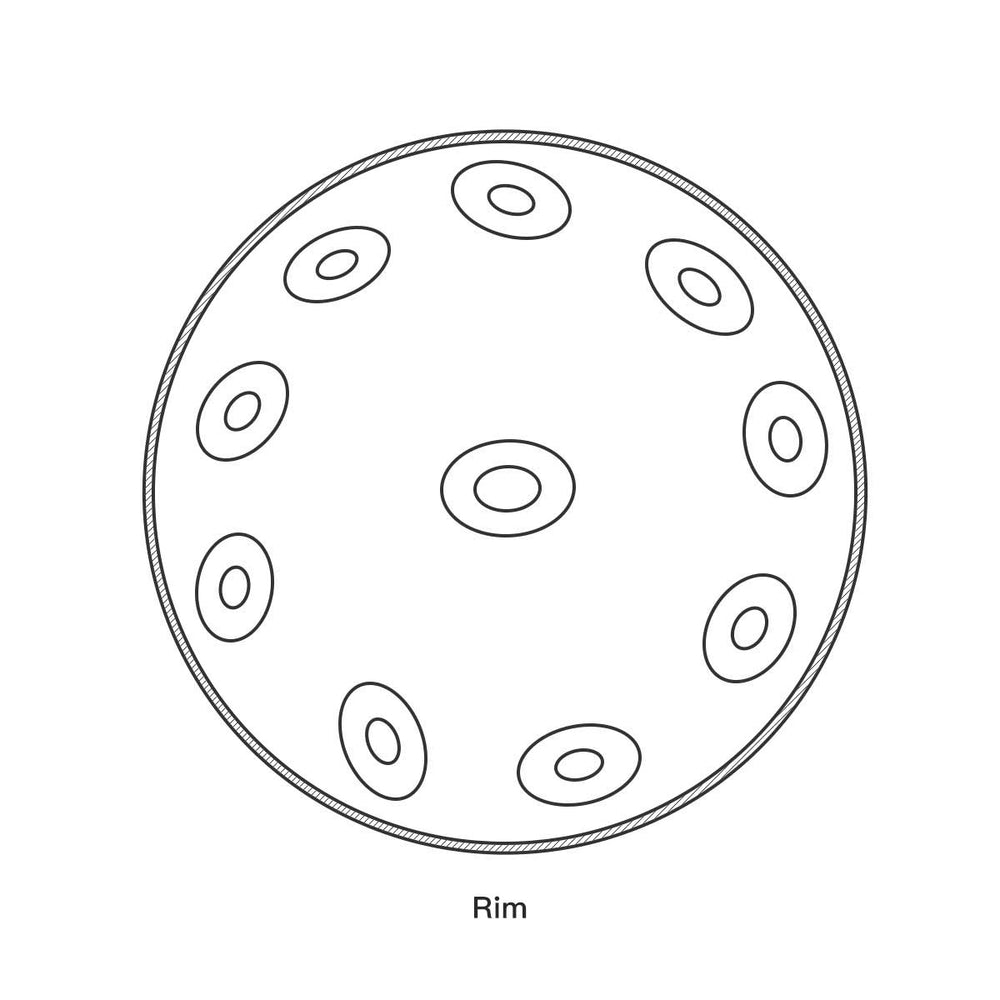
The Handpan is instantly recognizable due to its distinct, symmetrical structure. It is composed of two bowl-shaped metal shells permanently joined together, giving it an external appearance strikingly similar to a flying saucer.
This unique design is functional, dividing the instrument into two key areas: the playing surface (top shell) and the resonating chamber (bottom shell).
The Top Shell: The Primary Playing Surface
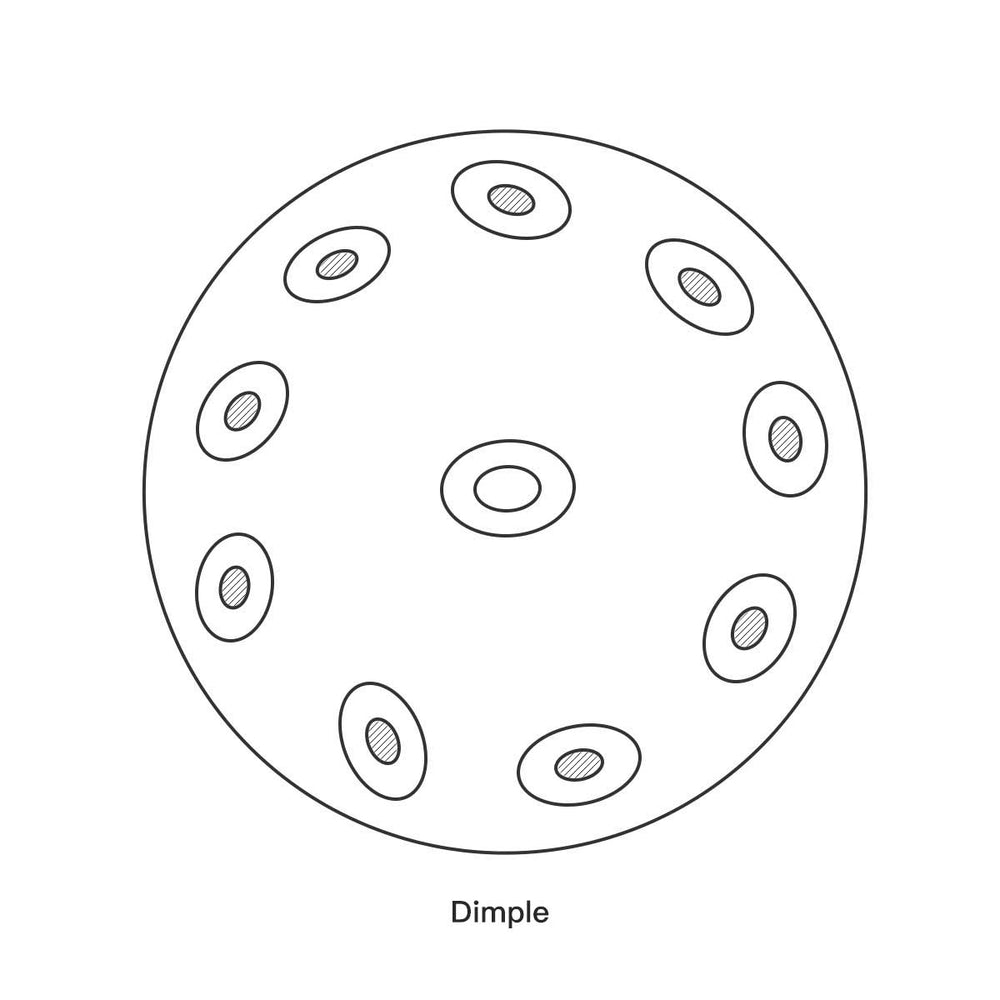
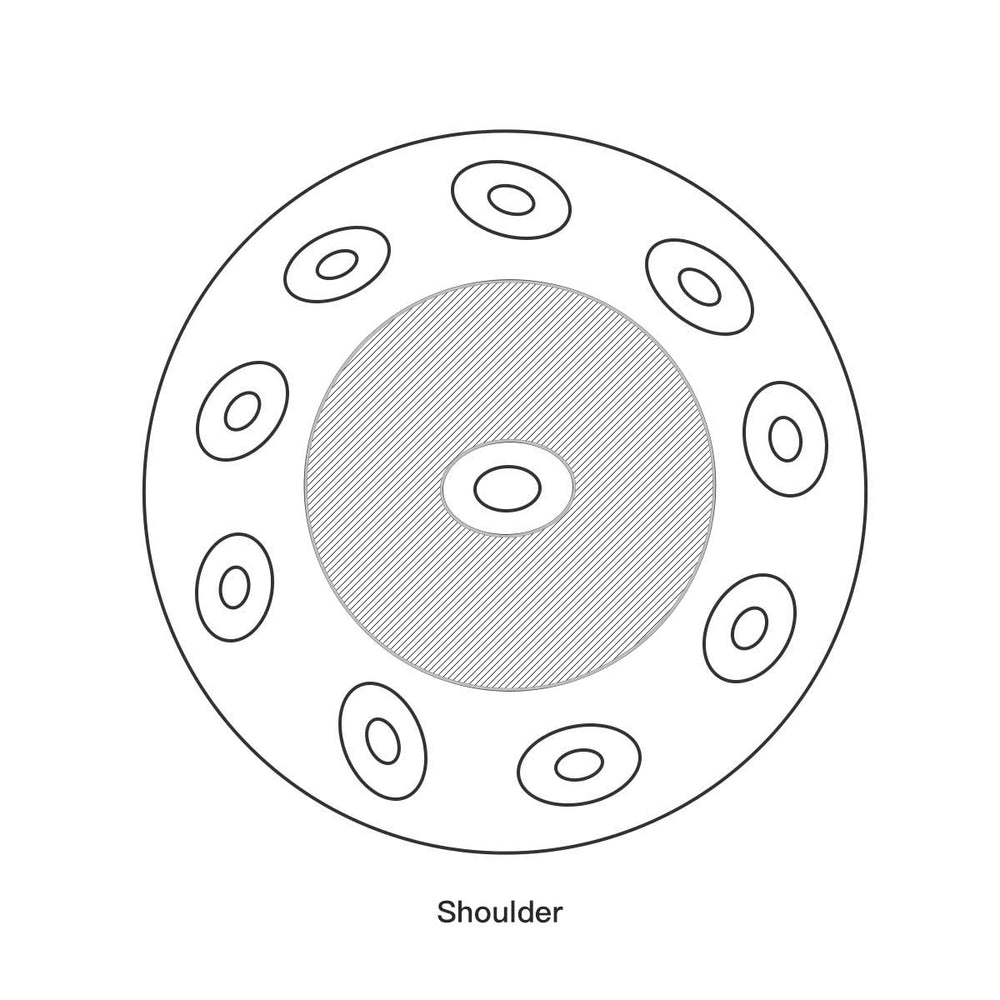
The top shell is the main playing surface where all the melodic notes are located. It typically features nine or more distinct tone areas.
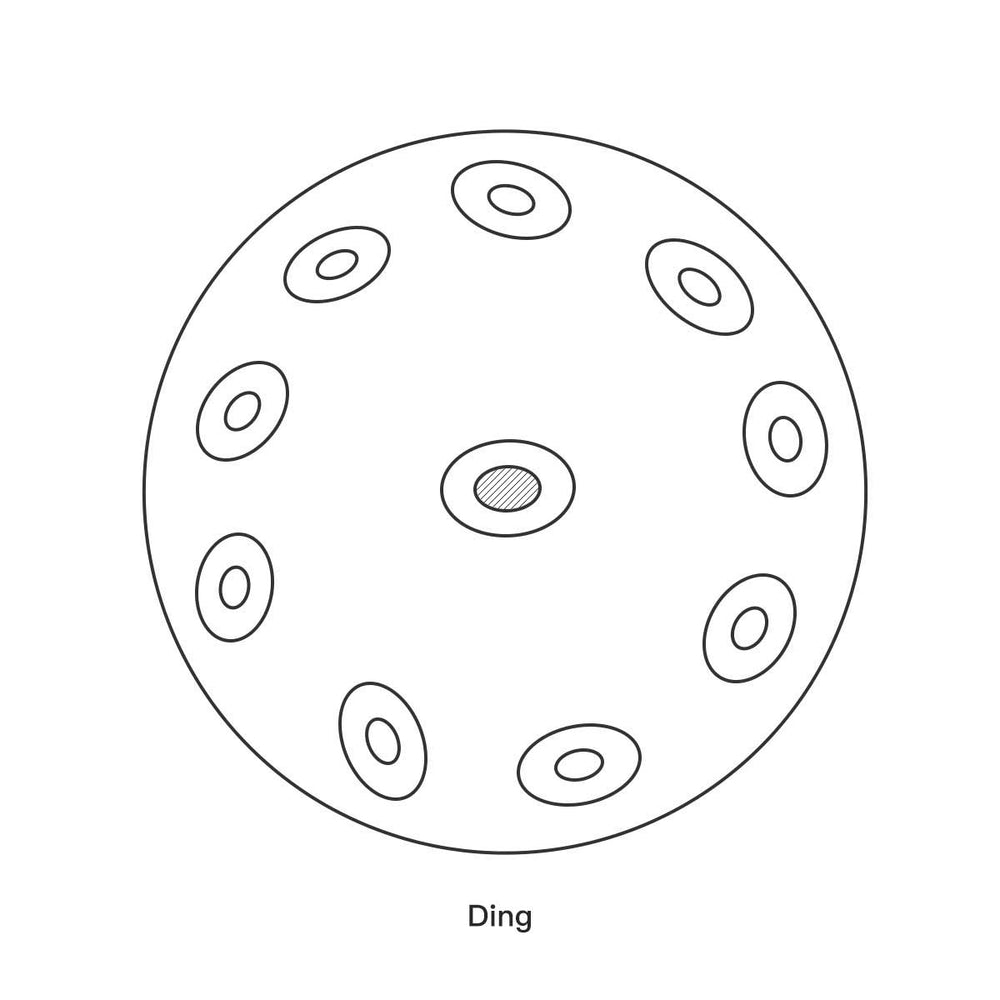
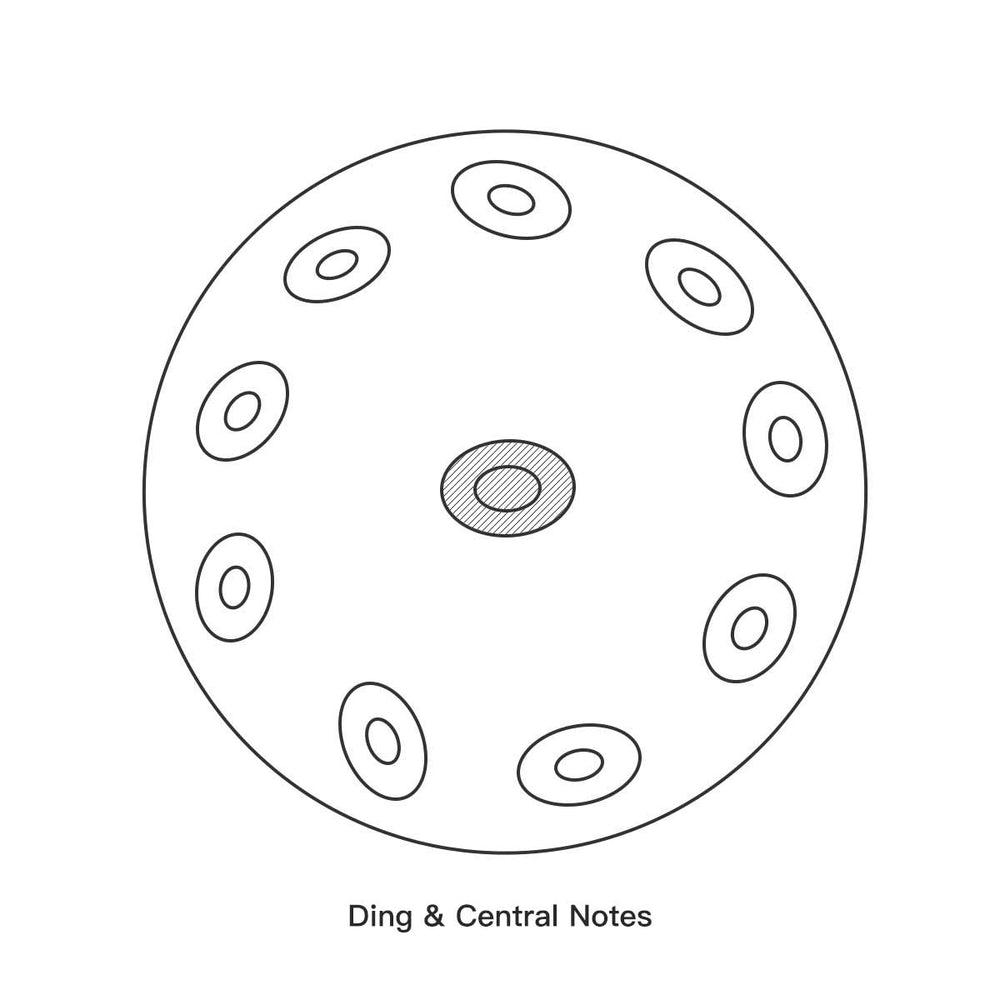
1. The Ding (The Center Note)
The most prominent feature of the top shell is the central, convex (raised) note known as the “Ding.”
-
Function: The Ding is usually the lowest note on the instrument and acts as the central anchor for the scale. It is a fundamental part of the instrument's sound structure and is often the first note struck when playing.
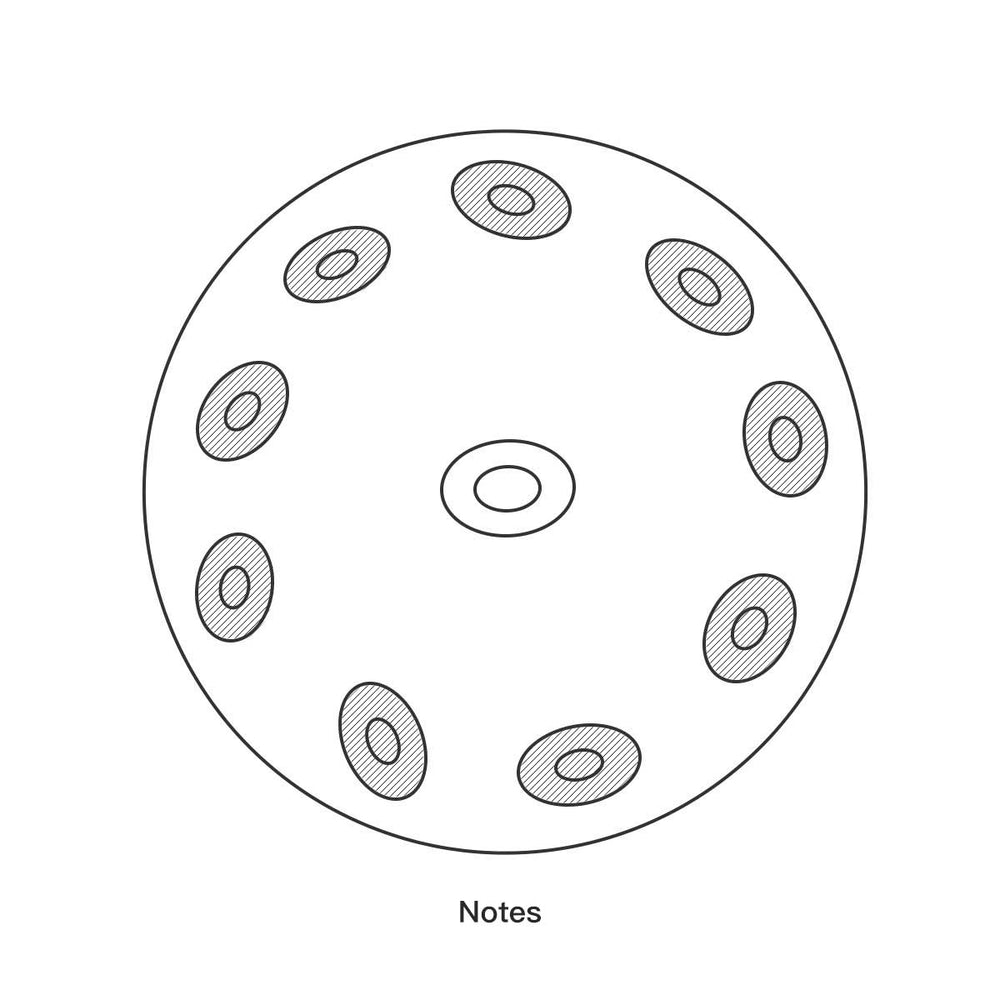
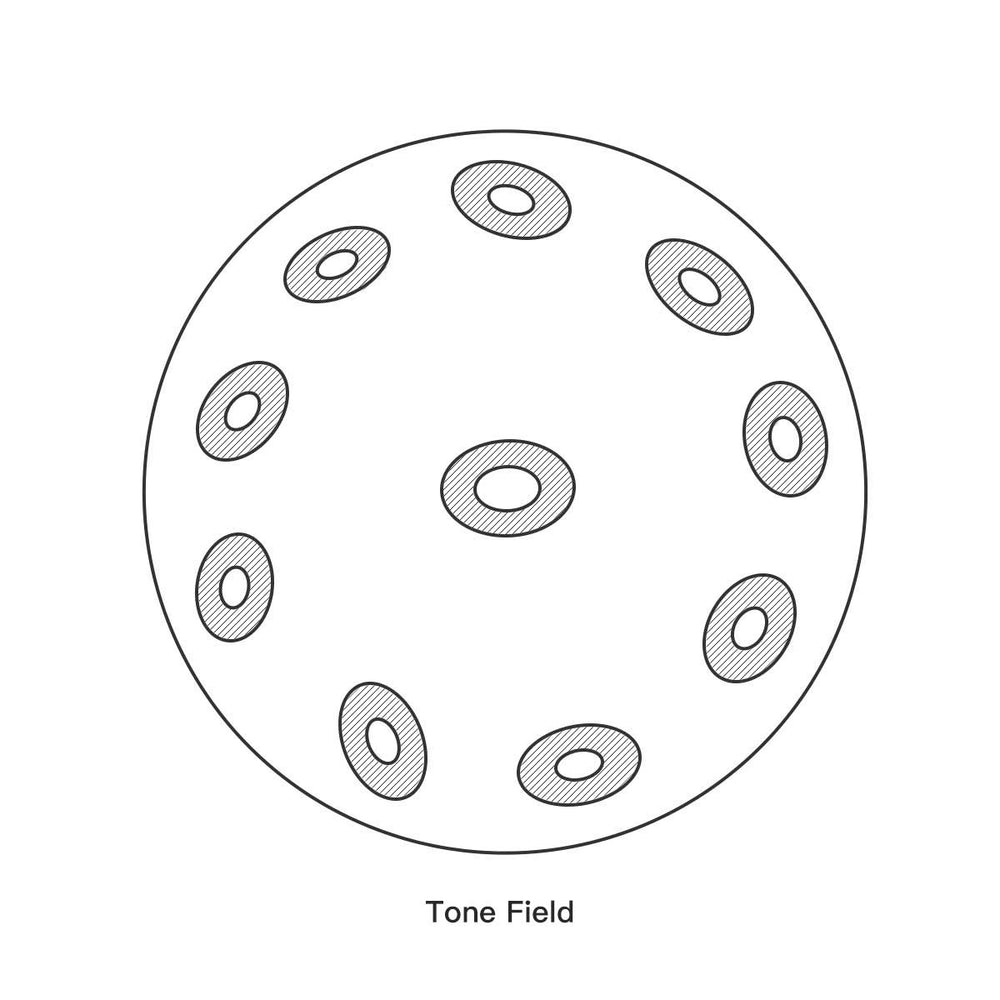
2. The Tone Fields (The Melody Notes)
Surrounding the Ding, the remaining tone areas are concave (sunken) depressions. These are the tone fields, and each is precision-tuned to produce a different pitch.
-
Pitch and Size: A simple rule of thumb applies to the tone fields: the larger the tone field’s surface area, the lower the note's pitch.
-
Layout: The notes are typically arranged in a "Z-shaped" pattern around the Ding, creating an ergonomic layout that allows the player to easily navigate between low and high notes to produce beautiful and fluid melodies.
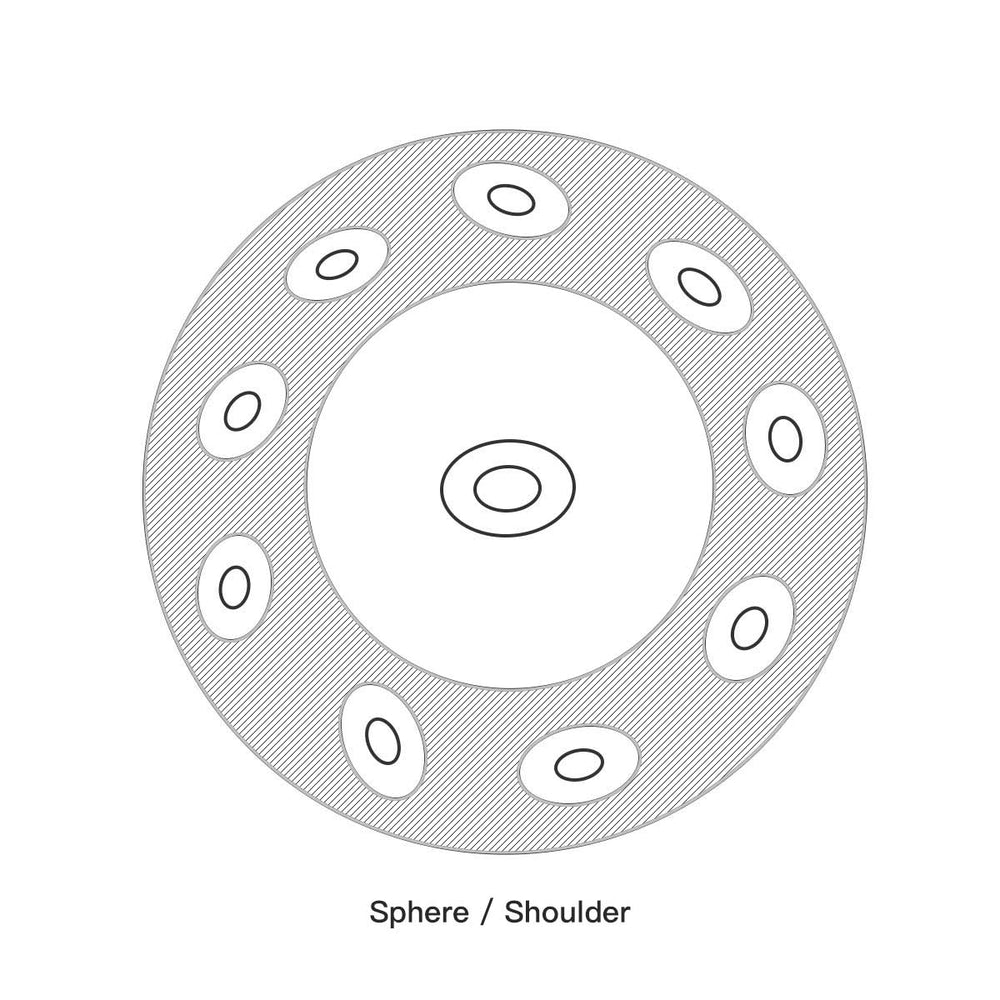
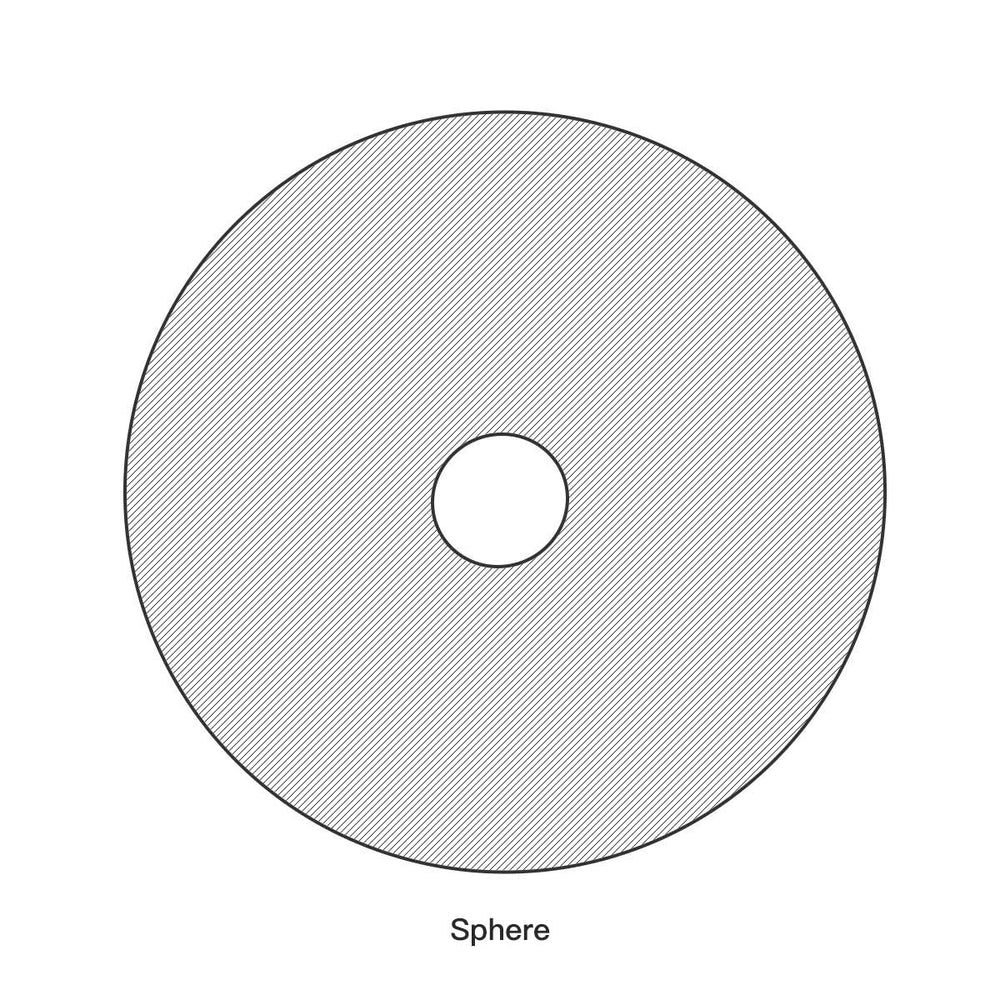
The Bottom Shell: The Resonator and the Gu
The bottom shell, while not directly played for melody, is essential for the instrument's rich resonance and volume.
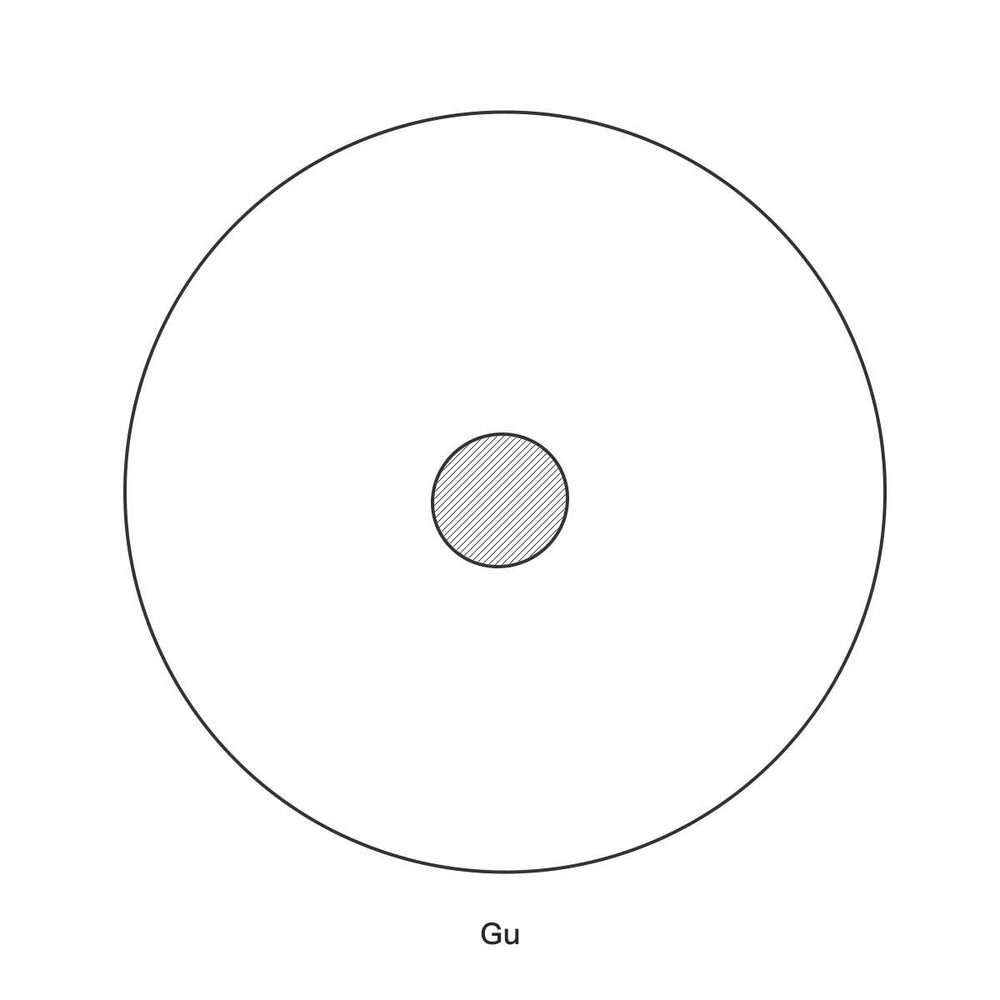
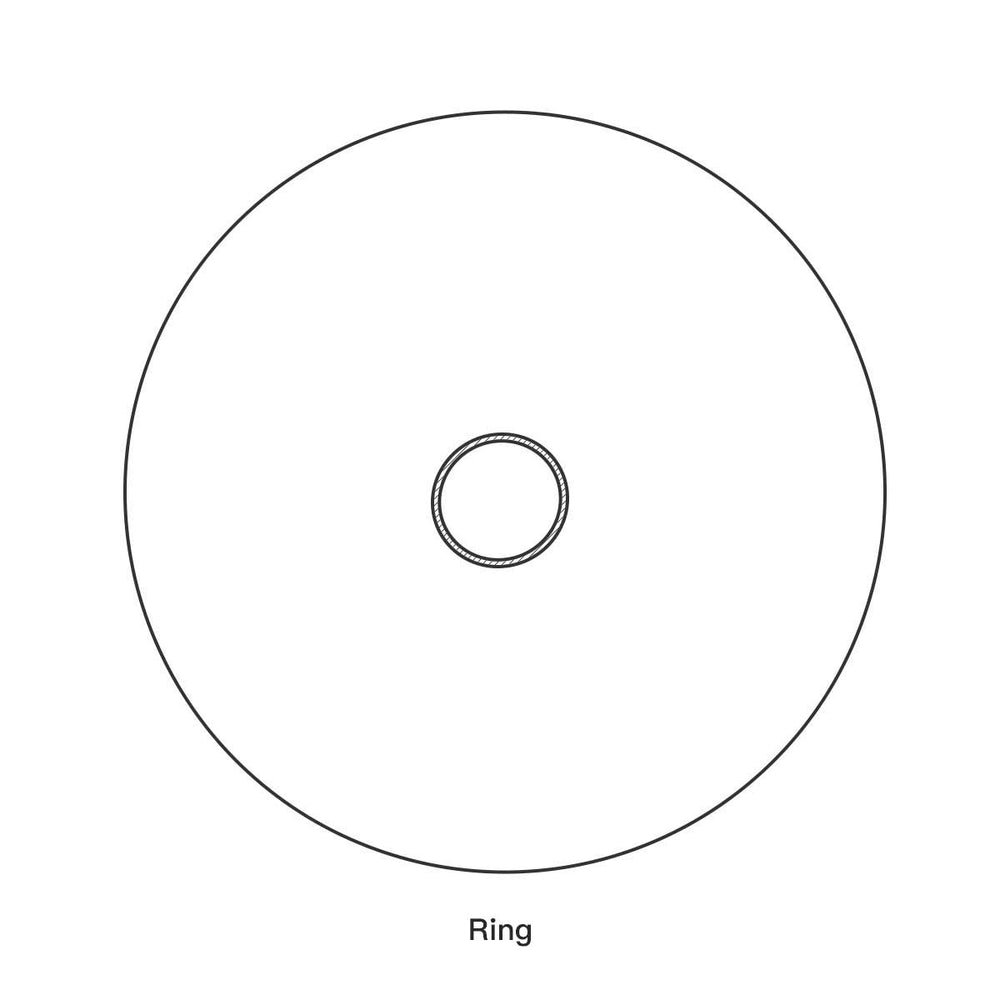
The Gu (The Resonance Hole)
Located at the very center of the Handpan's bottom shell is a circular opening known as the “Gu.”
-
Acoustic Principle: The Gu is strategically designed based on the Helmholtz Resonator principle. This principle allows the air inside the Handpan's chamber to vibrate and interact with the struck tone fields, enabling the instrument to achieve its full, sustaining volume and overall unique timbre.
-
Historical Inspiration: The creators of the original Hang, Felix Rohner and Sabina Schärer, derived inspiration for the Gu directly from the Indian clay pot drum, the Ghatam, reinforcing the Handpan’s percussive heritage.
Handpan Anatomy: Quick Reference
For easy reference, the Handpan’s key components are:
-
The Shells: Two metal hemispheres joined together.
-
The Ding: The central, convex tone field (the lowest note).
-
The Tone Fields: The surrounding concave note areas (the melody).
-
The Gu: The hole on the bottom shell, acting as the Helmholtz Resonator.
🎯 Deepening Your Handpan Journey: Ready for the Next Level?
You now have a solid understanding of the Handpan's anatomy—from the resonant Ding and the melodic Tone Fields to the acoustic role of the Gu. But a Handpan's structure is only half the story.
The instrument’s beautiful voice and lasting quality are profoundly influenced by its materials.
Continue Exploring Our Comprehensive Handpan Guides:
The journey into this captivating instrument continues.
Click below to dive into the technical details that separate a good Handpan from a great one:
Handpan Materials: Nitriding vs. Stainless Steel
Click here to understand the differences between nitrided steel and stainless steel, how the material choice impacts sound, and why it is crucial for maintenance and longevity.
Following that, explore these essential topics:
🛸 Guide to the Handpan: History, Origins, and Evolution
To know the fascinating history behind the Handpan and the Hang, you're ready to explore what makes these instruments truly magical.
Handpan Buying Guide: How to Choose the Perfect Handpan for You
Discover how to choose the perfect handpan with our beginner-friendly guide. Learn about scales, notes, materials, 440Hz vs 432Hz tuning, and tips for meditation, yoga, and relaxation.
Handpan Scales and Modes: Choosing Your Voice
Understand the world of scales—from Minor Kurd to Major—and how these musical modes influence the emotional quality of your music.
The Diverse Uses of the Handpan
Explore how the instrument is used in everything from meditation and sound healing to professional studio recordings and live performance.
Essential Handpan Care and Maintenance
Learn the best practices for cleaning, storage, and routine maintenance to protect your investment and preserve its sound quality for years to come.
Handpan Anatomy Diagram
Shaded Sections >>